IGCSE

|The Natural Environment Lesson's |
| 1.Earthquakes and Volcanoes |
|Content|
|Lessons|
| Lesson 1 |
| Lesson 2 |
| Lesson 3 |
 |  |
|---|---|
 |
Candidates should be able to:
Describe the main types and features of volcanoes and earthquakes Describe and explain the distribution of earthquakes and volcanoes
Describe the causes of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions and their effects on people and the environment
Demonstrate an understanding that volcanoes present hazards and offer opportunities for people
Explain what can be done to reduce the impacts of earthquakes and volcanoes
Further guidance
Types of volcanoes (including strato-volcanoes [composite cone] and shield volcano) Features of volcanoes (including crater, vent, magma chamber) Features of earthquakes (including epicentre, focus, magnitude) The global pattern of plates and their structure; an awareness of plate movements, subduction zones and their effects – constructive/divergent, destructive/convergent and conservative plate boundaries
Case Studies required for 2.1
• An earthquake
• A volcano
 |
|---|
|Reading/Lesson Resources|
|Student work|
| 2. Rivers |
| Content|
| Lessons|
| Lesson 1 |
| Lesson 2 |
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
|Reading|
| Lesson 3 |
| Lesson 4 |





|Revision|
Candidates should be able to:
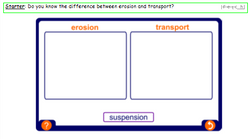
Explain the main hydrological characteristics and processes which operate in rivers and drainage basins Demonstrate an understanding of the work of a river in eroding, transporting and depositing
Describe and explain the formation of the landforms associated with these processes
Demonstrate an understanding that rivers present hazards and offer opportunities for people
Explain what can be done to manage the impacts of river flooding
Further guidance
Characteristics of rivers (including width, depth, speed of flow, discharge) and drainage basins (including watershed, tributary, confluence) Processes which operate in a drainage basin (including interception, infiltration, throughflow, groundwater flow, evaporation, overland flow)
Forms of river valleys – long profile and shape in cross-section, waterfalls, potholes, meanders, oxbow lakes, deltas, levées and flood plains Causes of hazards (including flooding and river erosion) Opportunities of living on a flood plain or a delta or near a river
Case Study required for 2.2
• The opportunities presented by a river or rivers, the associated hazards and their management
| 3. Coasts |
| Lessons|
| Content|
Candidates should be able to: Demonstrate an understanding of the work of the sea and wind in eroding, transporting and depositing
Describe and explain the formation of the landforms associated with these processes
Describe coral reefs and mangrove swamps and the conditions required for their development Demonstrate an understanding that coasts present hazards and offer opportunities for people Explain what can be done to manage the impacts of coastal erosion
Further guidance
Cliffs, wave-cut platforms, caves, arches, stacks, stumps, bay and headland coastlines, beaches, spits, and coastal sand dunes Hazards (including coastal erosion and tropical storms)
Case Study required for 2.3
• The opportunities presented by an area or areas of coastline, the associated hazards and their management
| Lesson 1 |
| Lesson 2 |
| Lesson 3 |
| Lesson 4 |
| Lesson 5 |
| Lesson 6 |
| Lesson 7 |
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |
|Reading|
| Video Revision |
| Revision |
| Student Work |
| 4. Weather & Climate |

| Content|
| Lessons|
|Reading|
|Student work|
 |  |
|---|---|
 |
| Lessons 1|
| Lessons 3|
| Lessons 2|
Candidates should be able to:
Describe how weather data are collected Make calculations using information from weather instruments Use and interpret graphs and other diagrams showing weather and climate data
Further guidance
Describe and explain the characteristics, siting and use made of a Stevenson Screen Rain gauge, maximum-minimum thermometer, wet-and-dry bulb thermometer (hygrometer), sunshine recorder, barometer, anemometer and wind vane, along with simple digital instruments which can be used for weather observations; observations of types and amounts of cloud























