
IGCSE
|Population and Settlements Lesson's |
|New Material|
| Lesson 1 |
| Lesson 2 |
| Lesson 3 |
| 1.Population |
|Content|
|Lessons|
|Fetch Booklet|
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |
| Lesson 4 |
| Lesson 5 |
| Lesson 6 |
| Lesson 7 |
| Lesson 8 |
| Lesson 10 |
| Lesson 9 |
| Lesson 11 |
The Fetch IGCSE Booklet helps you understand the expectations of the course and for you to track your progress.
Candidates should be able to:
Describe and give reasons for the rapid increase in the world’s population Show an understanding of over-population and under-population Understand the main causes of a change in population size Give reasons for contrasting rates of natural population change
Describe and evaluate population policies
Further guidance
Causes and consequences of over-population and under-population How birth rate, death rate and migration contribute to the population of a country increasing or declining Impacts of social, economic and other factors (including government policies, HIV/AIDS) on birth and death rates
Case Studies required for 1.1
• A country which is over-populated
• A country which is under-populated
• A country with a high rate of natural population growth
• A country with a low rate of population growth (or population decline)

|Case Study Cards|
|Reading/Lesson Resources|
|Revision|
|Student work|
| 2. Migration |
| Content|
| Lessons|
Candidates should be able to:
Explain and give reasons for population migration Demonstrate an understanding of the impacts of migration
Further guidance
Internal movements such as rural-urban migration, as well as international migrations, both voluntary and involuntary Positive and negative impacts on the destination and origin of the migrants, and on the migrants themselves
Case Study required for 1.2
• An international migration
Candidates should be able to:
Identify and give reasons for and implications of different types of population structure Further guidance Age/sex pyramids of countries at different levels of economic development
Case Study required for 1.3
• A country with a high dependent population
| Lesson 1 |
| Lesson 2 |
| Lesson 3 |
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
|Reading/Lesson Resources|
| Lesson 4 |
| Lesson 6 |
| Lesson 5 |
|Media|
|Student work|

| 3. Settlements |
| Lessons|
| Content|
 |  |
|---|---|
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
| Lesson 1 |
| Lesson 2 |
| Lesson 3 |
| Lesson 4 |
| Lesson 5 |
| Lesson 6 |
| Lesson 7 |
| Lesson 8 |
| Lesson 9 |
| Lesson 10 |
Candidates should be able to:
Explain the patterns of settlement Describe and explain the factors which may influence the sites, growth and functions of settlements
Give reasons for the hierarchy of settlements and services
Further guidance
Dispersed, linear, and nucleated settlement patterns Influence of physical factors (including relief, soil, water supply) and other factors (including accessibility, resources) High-, middle- and low-order settlements and services. Sphere of influence and threshold population
Case Study required for 1.5
• Settlement and service provision in an area
Candidates should be able to:
Describe and give reasons for the characteristics of, and changes in, land use in urban areas Explain the problems of urban areas, their causes and possible solutions
Further guidance
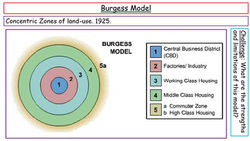
Land use zones including the Central Business District (CBD), residential areas, industrial areas and the rural-urban fringe of urban areas in countries at different levels of economic development The effect of change in land use and rapid urban growth in an urban area including the effects of urban sprawl Different types of pollution (air, noise, water, visual), inequality, housing issues, traffic congestion and conflicts over land use change
Case Study required for 1.6
• An urban area or urban areas
|Reading|
|Student Tinkercad project|
|Media|
|Student work|









































